What Are Meltdown And Spectre will be described in this article. Two of the most common hardware vulnerabilities in the world are Meltdown and Spectre, which were first identified in June 2017 and are still causing problems for us today. Computers, phones, tablets, wearables, cloud servers, and other devices are all impacted by Meltdown and Spectre. Learn what steps you can take immediately to protect yourself from these potentially disastrous breaches in digital security.
What Are Meltdown And Spectre
In this article, you can know about What Are Meltdown And Spectre here are the details below;
What are the Meltdown and Spectre vulnerabilities?
Almost all modern computer processors are vulnerable to the hardware flaws Meltdown and Spectre, which were unintentionally included during the construction of CPUs (central processing units). CPUs are essentially the brains of your gadgets; they carry out the “thinking” and “doing” involved in computing, i.e., they carry out your commands and maintain the operation of your programs.
This Article Contains:
- Meltdown Specter
- What is the number of individual variants?
- speculative performance
- Execution that is not in order
- Which goods are more vulnerable?
- AMD Intel
- IBM Arm
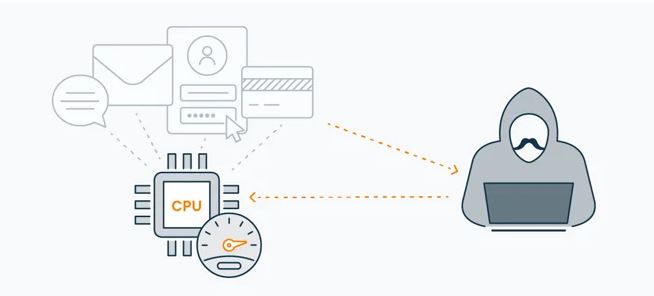
Hackers can read your processor’s “mind” while it’s “thinking” thanks to vulnerabilities in Meltdown and Spectre, which makes it possible for them to steal confidential information including passwords, bank account information, images, private papers, and more.
The susceptible CPUs, produced by Intel and other companies, are present in a wide range of gadgets, including servers, computers, smart devices, and industrial. In fact, it’s quite likely that you own one or more devices that are impacted by this security hole in Intel chips. The cybersecurity community has been startled since these security weaknesses were discovered, and analysts and developers are still in disbelief. Also check portable antivirus software for Windows
Almost all computer processors in use today are vulnerable to the hardware flaws Meltdown and Spectre, which were unintentionally included during the CPU design process.
Despite being found concurrently, Meltdown and Spectre are actually two distinct hardware security flaws with slightly different functionalities.
Meltdown
The majority of devices have “sandboxed” operating systems and programs, which keep the apps and OS apart and prevent them from accessing one other’s data or compromise the OS. Meltdown, formally identified by the Standard for Information Security Vulnerability Names as CVE-2017-5754, “melts” the barriers that typically separate applications from the operating system. The Intel, Apple, and certain IBM and ARM CPUs are impacted by the Meltdown vulnerability.
Spectre
Spectre, so named because it uses speculative execution, fools processors into carrying out orders that are ordinarily beyond of their purview, giving hackers access to confidential information kept in the memory of other programs. Spectre, also officially known as CVE-2017-5753 and CVE-2017-5715, is more difficult to attack than Meltdown and more difficult to mitigate. The CPUs made by Intel, Apple, AMD, ARM, and IBM are vulnerable to the Spectre exploit.
How many individual variants are there?
Thirteen Spectre variants and fourteen Meltdown variants have been found thus far by researchers. Spectre-NG (next generation) refers to Spectre variants that have been identified more recently. The only way to properly address the vulnerabilities is through a redesign of the hardware, as they are design defects. Regretfully, Intel and other chip makers will need a lot of time to fully modify and release their designs.
What are the risks?
The primary danger posed by Meltdown and Spectre is the loss of personal information. Given that the vulnerabilities can be used to access PCs, tablets, smartphones, smart devices, cloud servers, and other devices, this can be extremely harmful. Millions of people could be impacted by Meltdown and Spectre, in addition to corporations and nonprofits like healthcare institutions.
This implies that hackers might use Meltdown or Spectre to unleash global mayhem on a par with the WannaCry ransomware strain. Researchers in cybersecurity are understandably very concerned.
It’s crucial to ensure that your cybersecurity protection is strong in order to prevent vulnerabilities, exploits, and viruses of all kinds. Avast One employs AI and machine learning to identify and stop viruses and other malware before it can harm you. Additionally, you may use our Smart Scan tool to identify & address any security flaws in your system, such as obsolete software or dangerous passwords. Get it now to make sure that an additional layer of vital security is placed around your devices and important information.
How were the vulnerabilities discovered?
Researchers from Google Project Zero, Cyberus Technology, Graz University, and other universities found and reported Meltdown and Spectre. The flaws actually date back twenty years, but (in a bizarre coincidence), multiple separate researchers found them almost simultaneously.
How do Meltdown and Spectre work?
Remember that Central Processing Units are the “brains” of your devices, thus learning the fundamentals of CPU design is necessary before delving into the inner workings of Meltdown and Spectre.
All of the commands that enable apps to function on your device are carried out by CPUs. The pace at which computers could operate was formerly determined by their clock speed. The competition between the two major processor manufacturers, AMD and Intel, to raise clock speed was fierce. Speculative execution and out-of-order execution were created as a result of their efforts to find new methods of processing commands and data even quicker after they eventually reached a point where clock speeds could not be increased anymore.
speculative execution
By asking the CPU to predict or speculate as to what procedure or steps will be performed next, speculative execution speeds up processing. The CPU makes accurate guesses occasionally and incorrect ones other times. This means that when an incorrect guess results in a different command, the CPU may load a portion of a program or snippet of code and then reject it. Also check software tools
Through the use of the Spectre vulnerability, a hacker can take advantage of this predictive (speculative) process, breach security, and install malware that steals data by predicting the instructions that will be executed next and reading the stored memory used by those processes. Furthermore, Spectre has access to data that was imported arbitrarily and subsequently deleted, which occasionally contains private data like passwords or banking information.
Out-of-order execution
Out-of-order execution, also known as dynamic execution, enables CPUs to “think” ahead, much like its speculative counterpart. Out-of-order execution allows chips to execute whatever commands are available at any given time, regardless of any order, as opposed to waiting for all instructions to be completed in a conventional, linear manner.
By using speculative and out-of-order execution, CPUs can boost clock speed through predictions and timings that are manipulated by the Meltdown and Spectre vulnerabilities.By using speculative and out-of-order execution, CPUs can boost clock speed through predictions and timings that are manipulated by the Meltdown and Spectre vulnerabilities.
What products are most at risk?
Meltdown and Spectre impact a wide range of electronic devices because they are security issues in CPUs, or chips. They are specifically present in chips made by ARM, IBM, AMD, and Intel. As a result, a large range of consumer and commercial electronics are impacted by Meltdown and Spectre; in fact, practically all computers are susceptible.
Intel
Meltdown and Spectre are two vulnerabilities that affect Intel CPUs. Although software fixes were promptly published by Intel developers in an attempt to close the gaps, some of the solutions actually led to further problems. Although updated patches have been made available, comparable vulnerabilities may still be found unless significant modifications are made to the architecture of CPU hardware. Unfortunately, it may take years to develop new chip designs. Devices sold by Apple, Lenovo, HP, Dell, and other companies all use Intel CPUs.
AMD
Because AMD CPUs use privilege level protections in their paging design, they are susceptible to Spectre but not Meltdown. Products sold by Acer, Ryzen, Threadripper, Epyc, and other companies all use AMD CPUs.
IBM
IMB still produces microprocessors for servers, supercomputers, and data storage devices, however they no longer produce consumer CPUs. Spectre and Meltdown both have an impact on IBM.
ARM
Although ARM does not produce its own chips, it does license the architecture to other businesses. Thus, devices manufactured by Samsung, MediaTek, Qualcomm, and other companies use their CPU design. Meltdown and Spectre are two vulnerabilities that affect certain ARM-based microprocessors.
How will I know if my device is threatened?
You are almost definitely at risk due to the extensive range of devices that are affected by the Meltdown and Spectre vulnerabilities. It’s important to note, though, that neither vulnerability has been found to be exploited in the wild by cybersecurity experts. Intel and other researchers started working on patches as soon as they found the vulnerabilities (and coded their proof of concept).
Additionally, it would be difficult to determine whether you had fallen victim to Meltdown or Spectre as they don’t leave behind records the same way that conventional malware does. Even though the Meltdown and Spectre vulnerabilities are almost definitely present on your devices, it’s doubtful that you’ve been targeted. Fortunately, there are steps you can do to ensure that these malicious security holes never catch you off guard.
How to protect against Meltdown and Spectre
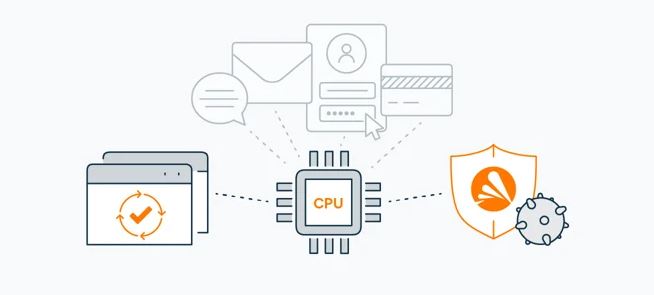
Antivirus software is unable to stop Meltdown and Spectre because they are hardware security flaws rather than true malware. Rather, the best defense against them is to maintain up-to-date browsers, operating systems, and devices. Updates with multiple patches (security fixes) have already been released to protect against Meltdown and Spectre.
Use strong antivirus software and keep all of your computers, devices, and browsers updated to protect yourself from vulnerabilities.Use strong antivirus software and keep all of your computers, devices, and browsers updated to protect yourself from vulnerabilities.
Like with any security hole, the real risk comes from what hackers can do with it rather than the flaw itself. Hackers specifically employ vulnerabilities to infect your machine with malware and viruses. Therefore, using a powerful antivirus program like Avast One is the best method to be safe from a potential exploit.
Fight malware that exploits Meltdown, Spectre, and other vulnerabilities
An antivirus program can guard against malware even while it cannot resolve a hardware vulnerability. The biggest worry regarding these security holes is the possibility that hackers and other bad actors may use them to their advantage, install malware, and steal data. In the end, malware is the problem here.
Fortunately, powerful antivirus software like Avast One can save you from all that fraud. With the help of our Smart Scan function, you can quickly strengthen your online defenses by identifying possible security risks including dubious add-ons, outdated software, weak passwords, and unsafe settings. Furthermore, Avast One offers security around-the-clock and will identify and stop any type of malware before it has a possibility to cause serious harm to your machine.





Add Comment